Work and energy
Work and energy
The following text is used only for teaching, research, scholarship, educational use and informative purpose following the fair use principles.
We thank the authors of the texts and the source web site that give us the opportunity to share their knowledge
Physics
Work and energy
Work and Energy Notes
Force is the agent of change, Energy is the measure of change and Work is the way of transferring energy form one system to another.
Work =  (the area underneath a force versus position graph from xo to xf)
(the area underneath a force versus position graph from xo to xf)
Where f is force and x is position
However, if the force is constant, then you only need to do:
W= F![]() x or F x cos q
x or F x cos q
But if the force isn’t constant, you need to do the integral or find the area under the curve. When you do the integral form, assume that the angle between the force and the distance is zero unless stated otherwise.
If the distance traveled and the force are perpendicular, than the work is zero.
Ex: There is no work done by the centripetal force of a ball being swung on a string. There is also no work being done by the normal force of a box sliding down or up an inclined plane.
Kinetic Energy is the energy an object possesses by virtue of its motion.
K= ½ m v2
(for linear motion)
The Work-Kinetic Energy Theorem states that if only conservative forces act, then
W=DK
Power is the rate of doing Work
P= ![]() (instantaneous power)
(instantaneous power)
P=![]() (average power)
(average power)
P = F![]() v = Fv cos q
v = Fv cos q
Mechanical Potential Energy is the stored energy of an object due to its position.
U = mgh
You can do work on an object and give it potential energy.
A conservative force is one where the total work it does on an object is zero when the particle moves around any closed path returning to its initial position (independent of the path taken).
Examples: force of a spring (elastic force), gravitational force
A non-conservative force is one where the total work it does on a object is not zero when the particle moves around any closed path returning to its initial position (the path taken does alter the amount of work!).
Examples: friction, a person pushing
For a conservative force
W= -DU = 
Which also means… Fx = -![]()
The force function is the negative first derivative of the potential energy function
From these equations we can derive
Ug = mgh (gravitational PE)
Us= ½ kx2 (elastic PE)
Potential Energy Curves
An object is in equilibrium when the net force acting on it is zero.
Stable Equilibrium is when a small displacement results in a restoring force that accelerates the object back towards equilibrium.
Unstable Equilibrium is when a small displacement results in a force that accelerates the object away from equilibrium.
Neutral Equilibrium is when a small displacement results in zero force and the object remains in equilibrium.
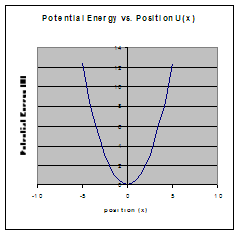
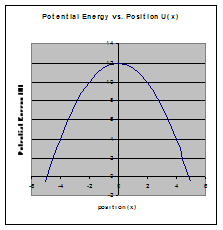
Stable equilibrium Unstable equilibrium
(minimum) (maximum)

Neutral Equilibrium
To find an equilibrium point and determine if it is stable or unstable:
- Set either the U’(x) = 0 and solve for x. This will tell you where the equilibrium points occur.
- To find out if it is a stable or unstable equilibrium point
- Graph the equation and take a look.
- Take the slope (first derivative) of the equation right before and right after where the maximum or minimum occurs.
- If the slope goes from positive to negative, that means it’s a maximum (unstable equilibrium)
- If the slope goes from negative to positive, that means it’s a minimum (stable equilibrium)
- Take U’’(x) (keep track of your positive and negative signs- don’t use F’(x) because the negative sign will affect your answer!)
- Substitute the number you found in part b for x.
- If U’’(x) > 0 it is in stable equilibrium (it is a minimum of U(x))
- If U’’(x) < 0 it is in unstable equilibrium (it is a maximum of U(x))
Conservation of Mechanical Energy
–Assuming no non-conservative forces act, the mechanical energy is conserved.
Total mechanical energy E= Uo + Ko
Uo + Ko = Uf + Kf
Remember that the potential energy can also have an elastic component as well as a gravitational component. Also, the kinetic energy can have a rotational as well as linear component. Make sure you include all the types and keep your reference point consistent.
When there are non-conservative forces acting, energy can be added or lost to the system through work by something like friction or you pushing an object. In this case
Uo + Ko + Wother = Uf + Kf
Work can be positive or negative. If the work is adding energy to the system then it’s positive. If it’s taking energy away from the system then it’s negative.
Source : http://www.groovytoo.com/robinson/AP/Work%20and%20Energy%20Notes.doc
Web site link: http://www.groovytoo.com/robinson/
Author : Ms. Robinson
Work and energy
Work and energy
Work and energy
This is the right place where find the answers to your questions like :
Who ? What ? When ? Where ? Why ? Which ? How ? What does Work and energy mean ? Which is the meaning of Work and energy?
Work and energy
Alanpedia.com from 1998 year by year new sites and innovations
Main page - Disclaimer - Contact us