Pressure formula notes
Pressure formula notes
The following text is used only for teaching, research, scholarship, educational use and informative purpose following the fair use principles.
We thank the authors of the texts and the source web site that give us the opportunity to share their knowledge
Physics
Pressure formula notes
Pressure
Pressure is defined as force per unit area. Pressure can be expressed as a relative pressure or an absolute pressure. The units of pressure are:
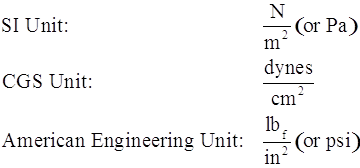
Chemical engineers are most often interested in pressures that are caused by a fluid.
- If fluid is flowing through a horizontal pipe and a leak develops. A force must be applied over the area of the hole that causes the leak. This pressure is called the fluid pressure (the force must be applied divided by the area of the hole). This is schematically shown in Figure 5.

Figure 5: Fluid pressure in a tank and a pipe
- If a vertical container contains a fluid, the mass of the fluid will exert a force on the base on the container. This pressure is called the hydrostatic pressure. Hydrostatic pressure is the pressure caused by the mass of a fluid. This is shown schematically in Figure 6.

Figure 6: Pressure at the base of fluid column (hydrostatic pressure)
Types of Pressures
a. Atmospheric pressure, ![]() , is the pressure caused by the weight of the earth’s atmosphere. Often atmospheric pressure is called Barometric Pressure.
, is the pressure caused by the weight of the earth’s atmosphere. Often atmospheric pressure is called Barometric Pressure.
b. Absolute pressure, ![]() , is the total pressure. An absolute pressure of 0 is a perfect vacuum. Absolute pressure must be used in all calculations unless a pressure difference is used.
, is the total pressure. An absolute pressure of 0 is a perfect vacuum. Absolute pressure must be used in all calculations unless a pressure difference is used.
c. Gauge Pressure, ![]() , is pressure relative to atmospheric pressure.
, is pressure relative to atmospheric pressure.
d. Vacuum is a gauge pressure that is a pressure below atmospheric pressure. It is used so that a positive number can be reported.
Absolute pressure, gauge pressure and the atmospheric pressure are related by the following expression:
![]()
The standard atmosphere is defined as the pressure equivalent to 760 mm of Hg at sea level and at ![]() . The unit for the standard pressure is the atmosphere, atm. Pressure equivalents to the standard atmosphere (atm) are:
. The unit for the standard pressure is the atmosphere, atm. Pressure equivalents to the standard atmosphere (atm) are:
The units, psi and atm, often carry a trailing “a” or “g” to indicate that the pressure is absolute or gauge pressure. Thus, by psig, we me gauge pressure in psi and by psia, we me absolute pressure in psi. So is the meaning of atma or atmg if nothing is noted otherwise.
Example:
A pressure gauge on a tank reads 20 psi. What is the gauge pressure?
Solution:
The gauge reads the gauge pressure directly. So, we must interpret the reading as gauge pressure and to avoid confusion, we should report the pressure as 20 psig instead of 20 psi.
Example:
A gauge on a tank reads 15 psi. What is the absolute pressure in the tank?
Solution:
![]()
Since atmospheric pressure was not given, we must assume it is 14.7psi. Thus, we find the absolute pressure in the tank as:

Example:
The pressure gauge on a tank reads 20. cm Hg vacuum. What is the absolute pressure in the tank?
Solution:
The gauge reads a vacuum gauge pressure directly. The pressure is below atmospheric, or is –20 cm Hg relative to atmospheric pressure. Thus, the absolute pressure is:

Pressure Sensing Devices
Some Pressure sensing devices are
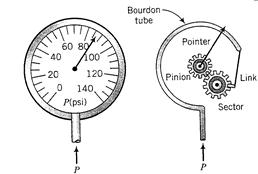 Bourdon gauge
Bourdon gauge- Diaphragm capsule
- Capacitance sensor
- Column of fluid
- Manometer
- Barometer
Figure 7: Bourdon gauge
A manometer is a U-shaped device that uses a fluid, which has a greater density than the other fluids in the process unit. Manometer operation is based on the fact that hydrostatic pressure at the same level in the same fluid must be the same in each leg. To understand how a manometer works, we must understand how to determine the hydrostatic pressure caused by a mass of a column of fluid. By definition of pressure:
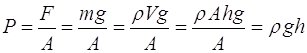
Whenever we need to determine the hydrostatic pressure caused by a mass of fluid, it’s simply: ![]()
Example:
What is the pressure (in kPa) caused by a 25.0 cm column of fluid (SG = 6.43) at sea level and ambient conditions?
Solution:
![]()
In SI units: 
Example:
What is the pressure (in psi), caused by a 6.34 ft column of mercury at ambient temperature in a location where  ?
?
Solution:
From Table B1, we find the specific gravity for Hg: ![]() .
.
The density of water (reference fluid): 
Manometers for Pressure and ![]() Measurement
Measurement
Three different arrangements of manometers are shown in Figure 8. These manometers can be used to measure a pressure using a column of a dense liquid.
- An open-ended manometer can give the gauge pressure.
- A differential manometer gives
 between 2 points. Note that the pressure decreases in the direction of flow. Why?
between 2 points. Note that the pressure decreases in the direction of flow. Why? - A closed-end manometer gives absolute pressure.
- A manometer, which has one leg, sealed and the other leg open measures atmospheric pressure. It is called a barometer.
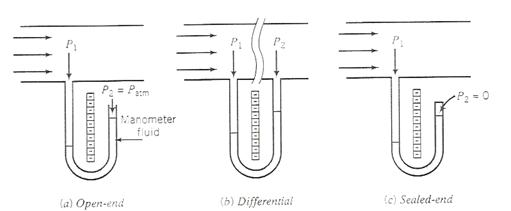
Figure 8: Arrangement of Manometers
The basics variables that need to be considered in manometry to measure pressure or pressure difference are shown in Figure 9.

Figure 9: Manometer variables
The line ‘ab’ is at the interface between the manometer fluid and the higher-pressure fluid. The hydrostatic pressure on each leg is the same at that point. It becomes our reference point. We do a pressure balance by equating the pressures on each leg.
Applying the above allows us to develop the general manometer equation as:
![]()
i.e.,
![]()
Example:
Determine the pressure drop across the orifice meter as shown below

Solution:
This is a differential manometer. Note that the hydrostatic pressure above the 32 mark is the same on both sides, it cancels out. The reference line to select is at the 10 mark. The manometer equation is
![]()
which simplifies to
![]()
We now can write the pressure difference across the orifice from the above equation as:
![]()
Substituting the appropriate known quantities, we get:

Source : http://www.ncat.edu/~chemeng/WORD%20docs/CHEN%20200/C200-f01-L06.doc
Web site link: http://www.ncat.edu
Author : not indicated on the source document of the above text
If you are the author of the text above and you not agree to share your knowledge for teaching, research, scholarship (for fair use as indicated in the United States copyrigh low) please send us an e-mail and we will remove your text quickly.
Pressure formula notes
Pressure formula notes
Pressure formula notes
This is the right place where find the answers to your questions like :
Who ? What ? When ? Where ? Why ? Which ? How ? What does Pressure formula notes mean ? Which is the meaning of Pressure formula notes?
Pressure formula notes physics notes
Alanpedia.com from 1998 year by year new sites and innovations
Main page - Disclaimer - Contact us