Measurement and density
Measurement and density
The following text is used only for teaching, research, scholarship, educational use and informative purpose following the fair use principles.
We thank the authors of the texts and the source web site that give us the opportunity to share their knowledge
Physics
Measurement and density
Syllabus
OP1 Measure length, mass, time and temperature (SI units); perform simple calculations based on these to find the derived quantities: area, volume, density.
Understand that units of measurement follow the SI system.
OP2 Measure mass and volume of a variety of solids and liquids and hence determine their densities.
OP3 Investigate flotation for a variety of solids and liquids in water and other liquids, and relate the results of this investigation to their densities.
Student Notes
There are literally hundreds of different units for some quantities like length and mass.
How different units of length can you think of?
It is important for scientists that everybody is using the same units.
Can you say why?
Scientists use units called S.I. Units
S.I. stands for Système International d'unités ; it is in french because it was the French who first promoted this system (you don’t need to know this).
What do you think Système International d'unités means ?
|
Length |
Mass |
Time |
Temperature |
Area |
Volume |
Speed |
S.I. units |
metres |
Kilograms |
seconds |
Degrees Celsius |
Metres squared |
Metres cubed |
metres per second |
Symbol |
m |
kg |
s |
0C |
m2 |
m3 |
m/s |
Equipment |
Metre stick, |
Electronic balance |
Clock, stopwatch |
Thermometer |
|
|
|
Other commonly-used instruments
Callipers |
Newton-meter |
Opisometer |
|
|
|
A callipers is used to measure the diameter of a cylinder |
A newton-meter is used to measure force (or weight) |
An opisometer is used to measure the length of a curved line |
.
Area of a regular object = length × width
Volume of a regular object = length × width × height
Instruments used to measure the volume of a liquid
1. Graduated cylinder
2. Pipette
3. Burette
Density

To measure density we simply use the following formula:
![]()
The unit of density is the kg/m3 (pronounced “kilogram per metre cubed”) or g/cm3
Density and Flotation
An object will float in a liquid if the density of the solid is less than the density of the liquid
e.g. plastics will float on water (or even iron cannonballs on mercury – see the YouTube clip).
A less dense liquid will float on top of a more dense liquid
e.g. oil will float on water.
Other commonly-used units:
Mass: grams (g)
Area: centimetres squared (cm2)
Volume: centimetres cubed (cm3)
1 litre = 1000 cm3
Experiments:
Measure mass and volume of a variety of solids and liquids and hence determine their densities.
- To measure the density of a regularly-shaped block
- To measure the density of an irregularly-shaped small stone
- To measure the density of an irregularly-shaped large stone
- To measure the density of a liquid
Summary of all the experiments
![]()
In each case to calculate the density we simply use the formula:

To measure the density of a regularly-shaped block
To find the mass - weigh it on an electronic balance.
To find the volume:
Volume = length × width × height
In this case the volume is 5 × 2 × 1 = 10 cm3.
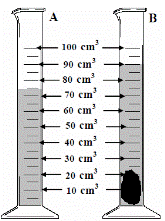
To measure the density of an irregularly-shaped small stone
To find the mass - weigh it on an electronic balance.
To find the volume:
Drop the stone into a graduated cylinder containing water and note the new volume.
To get the volume of the stone simply subtract the two readings.
In this case the volume = 90 – 75 = 15 cm3.
 To measure the density of an irregularly-shaped large stone
To measure the density of an irregularly-shaped large stone
To find the mass - weigh it on an electronic balance.
To find the volume:
Fill an overflow can up to the top and place an empty graduated cylinder under the spout.
Carefully drop the stone in (using a string so there is no splash).
Note the level of water in the overflow can.

To measure the density of a liquid
To find the mass:
Weigh an empty graduated cylinder, and then weigh the graduated cylinder after pouring water into it.
Then subtract the two readings.
To find the volume simply note the level of water in the graduated cylinder.
Exam Questions: Measurement and Units
 [2006 OL]
[2006 OL]
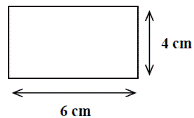
Find the area of the rectangle drawn on the right using the measurements given.
In what unit is the area measured?
m |
kg |
s |
- [2010 OL]
- Which of the following is the unit used to measure mass?
- Which of the following is the unit used to measure time?
 [2007 OL]
[2007 OL]  [2007]
[2007]- What is the name the piece of equipment shown on the right?
- Name a second item of laboratory equipment which enables more accurate measurements of volume to be made.
- [2006 OL] [2009 OL]
- The diagram shows a piece of equipment, labelled A, containing water. Name A.
- A stone was then added and a new volume was recorded as shown in B.
What was the volume of the stone in cm3?
![]()
- [2008 OL]
 Name and give one use for the piece of equipment shown in the diagram.
Name and give one use for the piece of equipment shown in the diagram.
- [2008 OL, 2006 OL]
- Name the piece of equipment drawn on the right.
- Give one use for this piece of equipment.
- [2008]
- Give one safety precaution taken by the pupil, shown in the photograph, while doing an experiment in a school laboratory.
- Describe a precaution, not shown in the photograph that you would take when heating a substance in a test tube in a school laboratory.

- [2009]
Name any two items of laboratory equipment shown in the diagram.
Density
- [2008 OL]
MASS |
- Complete the equation in the box below using the words on the right.
Density =
- If the mass of a stone is 20 g and the volume of the stone is 10 cm3, find the density of the stone.

- [2007 OL]
A block of metal has the measurements shown on the right.
The mass of the metal block is 21 g.
- Calculate the volume of the block.
- Calculate the density of the block.

- [2009 OL]
The mass of a metal block is 14.7 g. It has a volume of 7 cm3.
- Name the instrument you would use in the laboratory to find the mass of the block.
- Calculate the density of the block.
- What is the unit of density?
- [2009]
 A pupil measured the volume of a potato using the items of laboratory equipment, labelled A and B as shown in the diagram.
A pupil measured the volume of a potato using the items of laboratory equipment, labelled A and B as shown in the diagram.
- Name the items labelled A and B.
- The potato had mass 175 g and volume 125 cm3.
Calculate the density of the potato.
Give the units of density with your answer.
- Why did the potato sink in the water?
- [2010]
Why do icebergs float on water?
- [2007]
Ice floats on water but ice sinks in ethanol (an alcohol).
Use this information to compare the density of ice with
- the density of water;
- the density of ethanol.
Exam Solutions
- 6 × 4 = 24 cm2
- kg
- s
- Graduated cylinder
- Second item: burette/ pipette
- Graduated cylinder
- 90 – 75 = 15 cm3
- 15 cm3
- Thermometer; it is used to measure temperature
- Tripod
- To hold (support) objects (when heating)
- Wearing goggles/ looking through wall (side) of test tube/ tube in holder/ apparatus in centre of bench
- Point tube away/ add boiling chips to a liquid/ use small amounts/ lab coat/ heat gently/ screen/ gloves/ tie hair back…
- Bunsen burner/ tripod/ pipe clay triangle/ crucible/ tubing/ evaporating dish
- Density = Mass / Volume
- Density = 20 /10= 2 g/cm3
- 10 cm3
- 2.1 g cm-3
- Electronic balance / weighing scales
- Density = 14.7÷7 = 2.1
- Unit = g/cm3
- Item A is an overflow can
Item B is a graduated cylinder
- Density = 175/125 = 1.4 g/cm3
- Because it is denser than water
- They have a lower density than water.
- Ice is less dense than water
- Ice is more dense than ethanol
Extra Questions: Measurement and units
- What is the unit of (i) Length, (ii) Time, (iii) Mass, (iv) Area, (v) Volume?
- What is an opisometer used for?
- Name two instruments used to measure mass.
Extra Questions: Density
- What is meant by the term ‘density’?
- Draw a diagram of the apparatus used to measure the density of a regularly-shaped object.
- Draw a diagram of the apparatus used to measure the density of an irregular-shaped object.
- Draw a diagram of the apparatus used to measure the density of a liquid.
- A stone has a mass of 120 g and a volume of 20 cm3, what is the density of the stone?
- What is the density of an object which has a mass of 20 kg and whose volume is 4 m3?
A student measured the density of a number of substances. The results are shown in the table below. Identify two substances that would float in paraffin oil.
Substance |
Density (g/cm3) |
Cork |
0.3 |
Polystyrene |
0.03 |
Water |
1.0 |
Paraffin Oil |
0.7 |
Rubber |
1.1 |
Source : http://www.thephysicsteacher.ie/JC%20Science/JC%20Physics/Student%20Notes/1.%20Measurement%20and%20density.doc
Web site link: http://www.thephysicsteacher.ie
Author : not indicated on the source document of the above text
If you are the author of the text above and you not agree to share your knowledge for teaching, research, scholarship (for fair use as indicated in the United States copyrigh low) please send us an e-mail and we will remove your text quickly.
Measurement and density
Measurement and density
Measurement and density
This is the right place where find the answers to your questions like :
Who ? What ? When ? Where ? Why ? Which ? How ? What does Measurement and density mean ? Which is the meaning of Measurement and density?
Measurement and density physics notes
Alanpedia.com from 1998 year by year new sites and innovations
Main page - Disclaimer - Contact us


