Charles Augustin De Coulomb biography
CHARLES AUGUSTIN DE COULOMB biography
The following text is used only for teaching, research, scholarship, educational use and informative purpose following the fair use principles.
We thank the authors of the texts and the source web site that give us the opportunity to share their knowledge
Physics
CHARLES AUGUSTIN DE COULOMB biography
CHARLES AUGUSTIN DE COULOMB
Biography
Introduction
 |
During the life of Charles Augustin Coulomb, he would play important roles in the developments in physics, engineering, and experimental instruments. Coulomb was born in 1736 in the Languedoc region of France, but spent much of his early life in Paris and Montpellier. In 1760, at the age of 24 he was accepted into Ecole du Genie, an army engineering school in France. Once he was completed with school, he was first deployed to Brest as a military engineer. In 1764, he was sent to Martinique in the West Indies. There he was put in charge of building the new Fort Bourbon to attempt to make the island more secure. While in the West Indies, Coulomb would demonstrate his engineering skills and technical knowledge which he would later recall in his memoirs.
|
Image from: http://www.geocities.com/bioelectrochemistry/coulomb.htm |
|
The weather of Martinique was not hospitable to Coulomb. He was ill during most of his tour of duty there. After nine years, he was forced to return to France because these health issues.
Upon returning to France, Coulomb would take an interest in the recent research on electricity. That curiosity would eventually lead to the development of the torsion balance and the discovery of the relation which would become known as Coulomb's Law.
Historical Context
When Coulomb began his research into electric force (which would become known as Coulomb's law), Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation had already discovered. As it would turn out electrical forces would parallel Newton's discovery in many ways. In, both, Coulomb's law and Newton's law of universal gravitation, force is proportional to the inverse squared of the distance.
Coulomb's work would become one of the first cases where electric charge was measured quantitatively. In the 1740's electricity was beginning to become well know. By the 1750's, Benjamin Franklin's had shown that lightning was an electrical phenomenon thereby proving that that electricity did exist in nature. Franklin's work became an inspiration to others and spawned research into the study of electricity and measurement of it.
Instruments which could indicate electricity had existed since the 1730's, however these tools were of qualitative nature and did not approach real quantitative measurements. John Canton introduced an improved electrical indicator in 1753. Others, such as Tiberius Cavallo of Italy, concentrated their efforts atmospheric electricity, producing tools which could indicate the presence of electricity, but, like Canton’s electrical indicator, these tools were a long way from quantitative measurements.
Coulomb's Law
Coulomb is perhaps most famous for the law of physics bearing his name. Coulomb's law (Equation 1) describes the relationship between force, charge and distance. In 1785, Coulomb published a paper describing the torsion balance. This paper would become the first of a series of seven papers that Coulomb would have published on the topics of magnetism and electricity.
The torsion balance allowed Coulomb to make more precise measurements of force than anyone prior to that time.
Several other researchers, including Henry Cavendish, Joseph Priestly, and Charles Stanhope did similar work related to electrostatics. In fact, independently Henry Cavendish had determined experimentally the electric force was an inverse square law around the same time. However Cavendish never published his results or experiments, so it was not until 1879 that this fact was discovered by James Maxwell. Priestly's work with electrical repulsion served as the basis for Coulomb's research.
Equation 1-Coulomb's Law

Coulomb's law says the electrical force between two charges (q1) and (q2) is proportional to the product of the two charges divided by the distance between the two charges squared (see Equation 1 above). The torsion balance which Coulomb invented, allowed him to accurately measure electric forces and thereby establish this relationship. Since the charges q can be either positive or negative, Coulomb's law implies that the resultant force can be either attractive or repulsive. Figure 1 illustrates this fact.
Figure 1- Opposites Attract / Similar Charges Repel
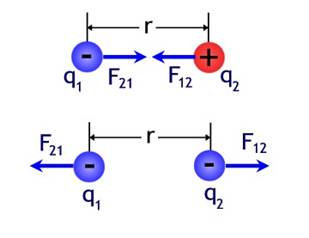
Image by Don Bahls based on Serway Figure 23.6
Adapted from http://ffden-2.phys.uaf.edu/212fall_2003.web.dir/don_bahls/coulombs_law.html on October 16, 2008.
Source : http://teachers2.wcs.edu/high/bhs/robertom/Lists/Calendar/Attachments/421/CHARLES%20AUGUSTIN%20DE%20COULOMB%20Biography.doc
Web site link: http://teachers2.wcs.edu/
Author : not indicated on the source document of the above text
If you are the author of the text above and you not agree to share your knowledge for teaching, research, scholarship (for fair use as indicated in the United States copyrigh low) please send us an e-mail and we will remove your text quickly.
CHARLES AUGUSTIN DE COULOMB biography
CHARLES AUGUSTIN DE COULOMB biography
Charles Augustin De Coulomb biography
This is the right place where find the answers to your questions like :
Who ? What ? When ? Where ? Why ? Which ? How ? What does CHARLES AUGUSTIN DE COULOMB biography mean ? Which is the meaning of CHARLES AUGUSTIN DE COULOMB biography?
CHARLES AUGUSTIN DE COULOMB biography physics notes
Alanpedia.com from 1998 year by year new sites and innovations
Main page - Disclaimer - Contact us